Your Best Shot at Strategic Trace Mineral Supplementation
Supports successful transitions



Supports a healthy immune system
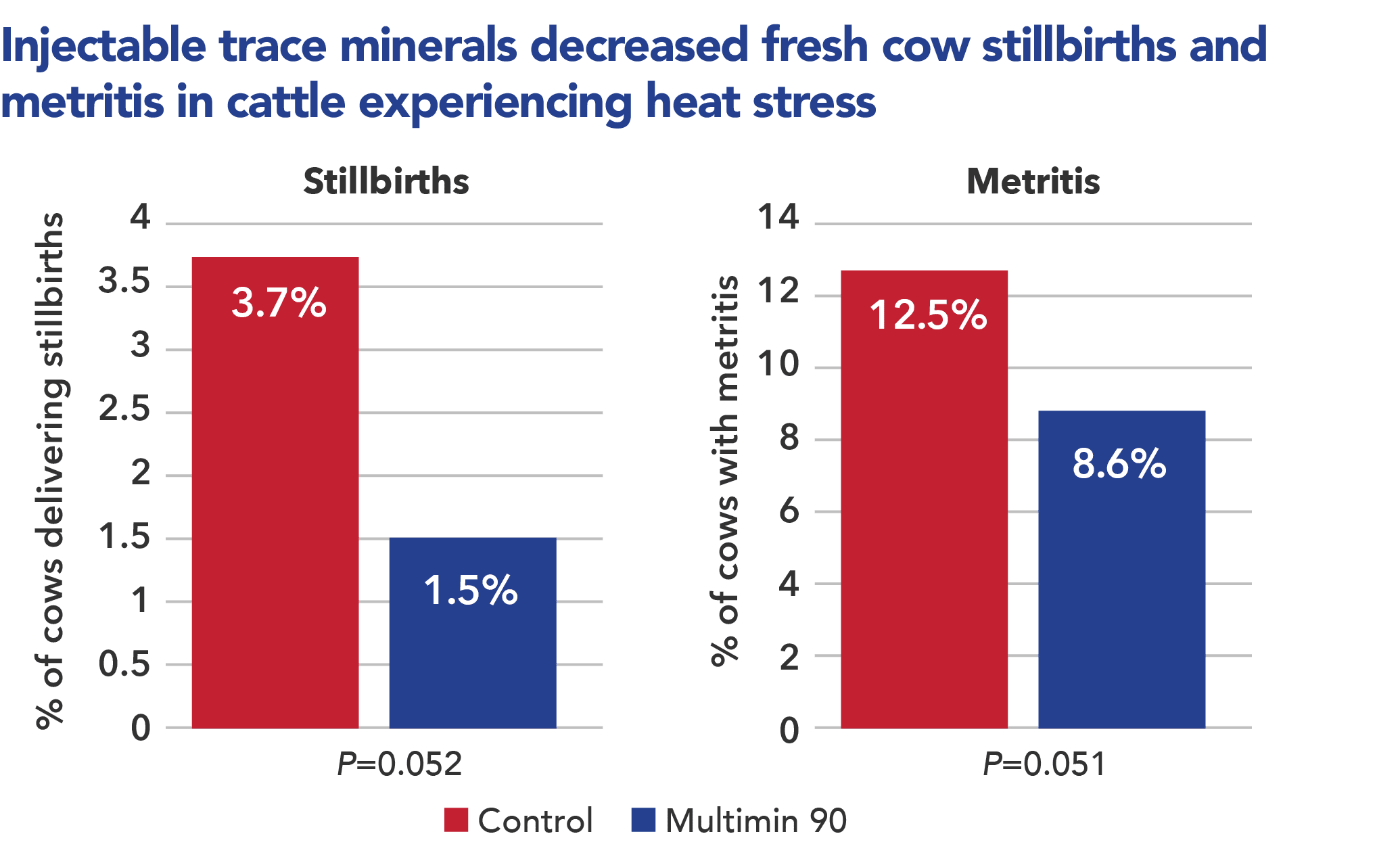
A large pen study conducted in Texas evaluated dairy cows through heat stress. Research results4 indicated that strategic trace mineral supplementation with Multimin 90 supported the immune system. The results also indicated that supplemented cows had:
- Reduced metritis cases
- Reduced stillbirths
Quickly replenishes trace minerals in the cow after in utero transfer to the calf
Research findings indicated that mineral levels decreased by approximately 30% at calving. University research results1 showed that Multimin 90 caused mineral levels to peak in the blood in 8–10 hours, with increases in liver levels within 24 hours post injection.
Supports udder health
The average case of clinical mastitis in the United States costs at least $400, including both direct costs, such as therapeutics or non-saleable milk, and indirect costs, such as future production or reproductive loss.5
University research results showed5 that when a single injection of Multimin 90 was given to dairy cows with elevated somatic cell counts, there was reduced incidence of chronic clinical mastitis, particularly in first lactation cows. Additionally, in cows with three or more lactations, subclinical mastitis treatment success was increased.
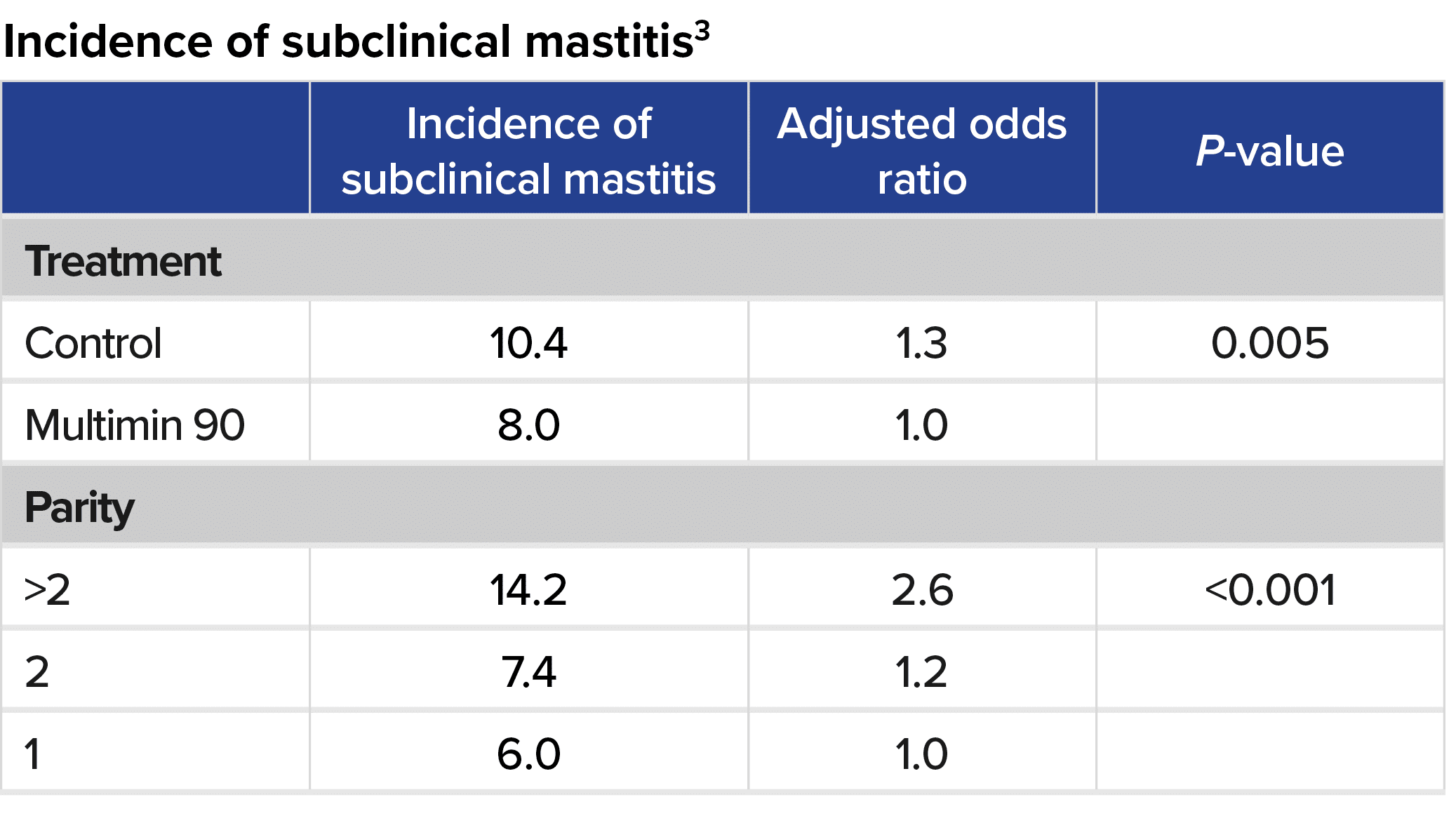
In another university study, research results showed3 a reduction in somatic cell counts, decreased clinical mastitis in multi-lactation cows, and decreased subclinical mastitis when cows were supplemented with zinc, copper, manganese and selenium by Multimin 90 injection at dry-off, 30 days pre-calving, and 35 days in milk.